For quotations, please use our online quotation form, and you may also contact us by
service@kendallscientific.com
+1-888.733.6849 (Toll-free)
+1-617.299.7367 (Int’l))
+1-888.733.6849
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours, Monday through Friday to assist you.| Reactivity | Human |
| Tested applications | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Calculated MW | 95kDa |
| Observed MW | Refer to figures |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human SECISBP2 |
| Storage Buffer | Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Concentration | j |
| Synonym | SBP2; |
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cells, using SECISBP2 antibody.

Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver injury using SECISBP2 antibody at dilution of 1:200 (40x lens).

Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma using SECISBP2 antibody at dilution of 1:200 (40x lens).

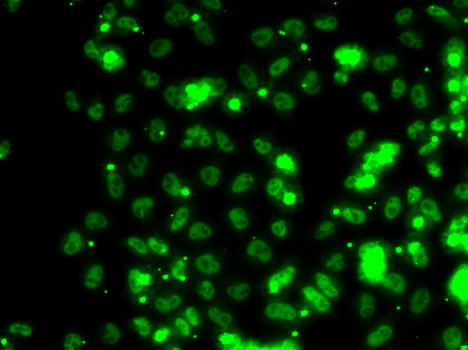
Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cell using SECISBP2 antibody.
The incorporation of selenocysteine into a protein requires the concerted action of an mRNA element called a sec insertion sequence (SECIS), a selenocysteine-specific translation elongation factor and a SECIS binding protein. With these elements in place, a UGA codon can be decoded as selenocysteine. The gene described in this record encodes a nuclear protein that functions as a SECIS binding protein. Mutations in this gene have been associated with a reduction in activity of a specific thyroxine deiodinase, a selenocysteine-containing enzyme, and abnormal thyroid hormone metabolism. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
N/A